Pc Bottleneck Calculator
Our tool quickly analyzes your CPU and GPU to detect potential bottlenecks, and optimize your PC for peak gaming and productivity.
Result
Performance Analysis:
Select components and click analyze to see detailed analysis.
A bottleneck calculator helps you understand how balanced your PC components are. It shows whether your CPU or GPU is limiting overall performance. This information is useful for gamers, editors, and general PC users who want smoother results. It also helps identify performance issues before making upgrades.
Many users face low FPS, stuttering, or slow system response without knowing the real cause. In most cases, these problems are linked to hardware imbalance. This page explains what a bottleneck is in simple terms and how the calculator works. It also guides you on reading results and improving performance.
What Is a PC Bottleneck?
A PC bottleneck happens when one hardware component limits the performance of the rest of the system. In most cases, this occurs between the processor and the graphics card because both parts must work together continuously.
For example, a powerful GPU cannot perform well if the CPU is too slow to support it. In the same way, a strong CPU cannot reach its full potential if the GPU is outdated. When parts are mismatched, your PC cannot use its full power.
A bottleneck does not mean your PC is bad. It means your PC is unbalanced.
What Is a Bottleneck Calculator?
A bottleneck calculator is a tool that estimates the performance imbalance between PC components.
It mainly focuses on CPU and GPU interaction.
The tool considers:
- Processor performance
- Graphics card performance
- Screen resolution
- General workload type
The final result is shown as a percentage.
This percentage helps you understand how much one component may limit the other.
How to Use the PC Bottleneck Calculator
Using the calculator is simple and only takes a few seconds. You select your processor, choose your graphics card, and pick your screen resolution. The tool then analyzes how balanced your components are and generates a bottleneck estimate.
This result helps you understand whether your system is well-matched or if one part may be limiting performance. It gives you a clear starting point before optimizing or upgrading your PC.
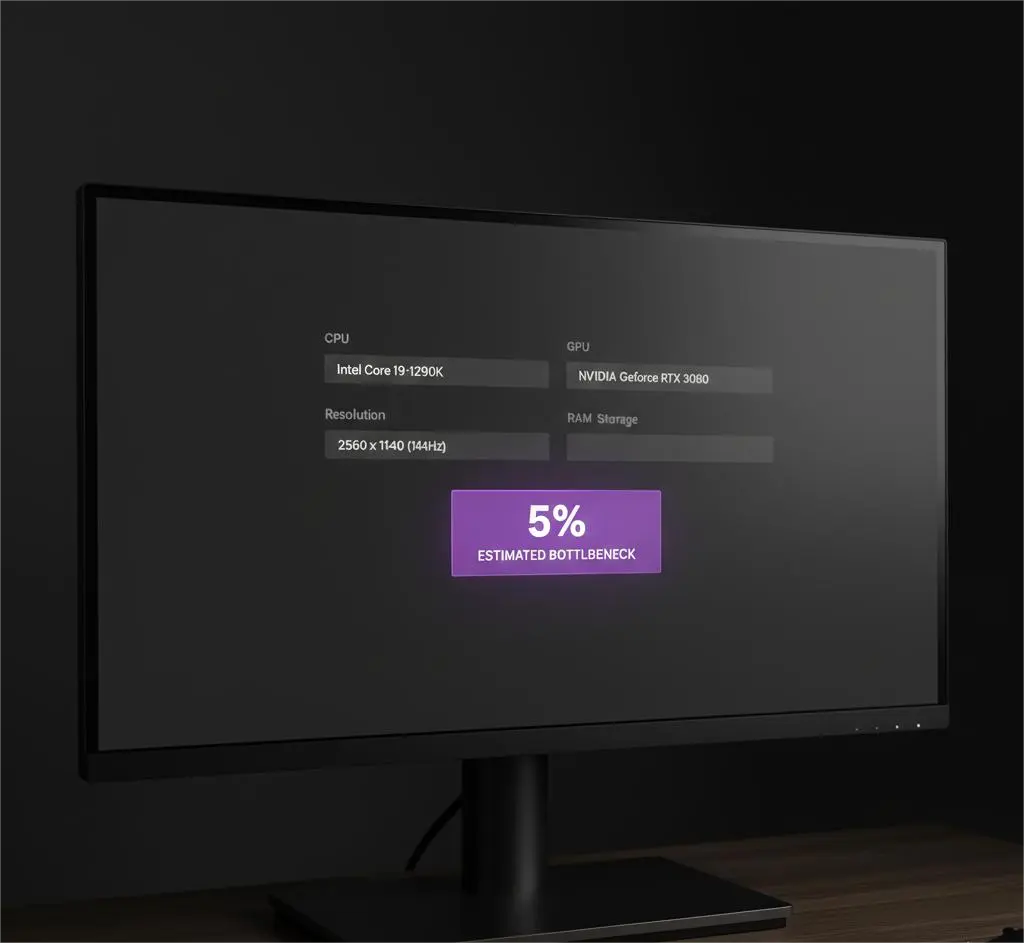
Basic usage steps:
- Select your CPU
- Select your GPU
- Choose your resolution
- Run the calculation
- Review the bottleneck result
This result is an estimate, not an exact measurement. Real-world results can vary depending on software, settings, and background tasks.
What the Calculator Actually Does
The PC Bottleneck Calculator estimates the performance relationship between your CPU and GPU. These two components work together in nearly every game and application, which makes their balance critical.
The calculator compares relative performance data and adjusts results based on resolution. It then produces a bottleneck percentage that represents how often one component may be waiting for another.
This value is meant to guide decisions, not replace real testing.
Why Bottlenecks Matter for Performance
Bottlenecks directly affect how your PC feels and performs. They often cause low or unstable FPS, stuttering, delayed responses, and poor multitasking performance.
Common issues include:
- Low frame rates
- Stuttering during gameplay
- High CPU usage with low GPU usage
- Longer load times
- Poor performance in editing or rendering tasks
Understanding bottlenecks helps you fix the root problem rather than upgrading the wrong part.
Key Factors That Affect Bottlenecks
Several elements decide where a bottleneck appears. The CPU handles calculations, physics, logic, and background processes, which makes it especially important at lower resolutions. The GPU is responsible for rendering visuals and becomes more important as resolution increases.
Screen resolution changes how work is divided between components. RAM capacity and speed affect smoothness and multitasking, while storage influences load times and overall system responsiveness. Cooling and thermals also matter because overheating can force components to slow down.
Main factors that affect bottlenecks
CPU Performance
The CPU handles game logic, physics, and background processes.
A weak CPU can limit performance, especially at lower resolutions.
GPU Performance
The GPU handles rendering and visual effects.
At higher resolutions, GPU performance becomes more important.
Screen Resolution
Resolution changes how work is distributed.
- 1080p puts more load on the CPU
- 1440p is more balanced
- 4K is mostly GPU-dependent
RAM and Storage
Slow or insufficient RAM can reduce performance in some cases.
Storage mainly affects load times, not FPS.
Cooling and Thermals
Poor cooling can cause thermal throttling.
This reduces component speed and creates performance limits.
Types of Bottlenecks Explained
A CPU bottleneck occurs when the processor cannot keep up with the graphics card, often resulting in high CPU usage and unstable performance. A GPU bottleneck happens when the graphics card reaches its limits, which is common at higher resolutions and ultra settings.
RAM bottlenecks occur when memory is insufficient or too slow, causing stutters and multitasking issues. Storage bottlenecks mainly affect boot and load times, but they can also impact overall system smoothness.
Common bottleneck types:
CPU Bottleneck
A CPU bottleneck occurs when the processor cannot keep up with the GPU.
This often results in high CPU usage and low GPU usage.
GPU Bottleneck
A GPU bottleneck happens when the graphics card limits performance.
This is common at high resolutions like 4K.
RAM Bottleneck
Insufficient or slow RAM can cause stutters and slowdowns.
This usually affects multitasking and newer games.
Storage Bottleneck
Slow storage increases load times.
It rarely affects in-game FPS.
How to Interpret Your Bottleneck Results
The bottleneck percentage helps estimate how balanced your system is. Lower values usually indicate a well-matched PC, while higher values suggest that one part may be strongly limiting performance.
General guideline:
- 0–5% → Very balanced system
- 5–10% → Minor bottleneck
- 10–20% → Noticeable bottleneck
- 20%+ → Strong performance limitation
A small bottleneck is normal.
No system is perfectly balanced.
Suggested table structure
| Bottleneck Percentage | Meaning | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 0–5% | Well-balanced system | No noticeable issues |
| 5–10% | Minor bottleneck | Usually acceptable |
| 10–20% | Moderate bottleneck | Performance loss possible |
| 20%+ | Severe bottleneck | Upgrade recommended |
What the Bottleneck Percentage Really Means
The bottleneck number does not represent direct FPS loss. A 10% bottleneck does not mean 10% lower performance. Instead, it estimates how often one component waits for another. Actual performance depends on:
- Game engine
- Graphics settings
- Drivers
- Background software
Always use the result as guidance, not a guarantee.
Real-World Performance Scenarios

At 1080p, games depend more on CPU power, which makes CPU bottlenecks more common. Even high-end GPUs can become CPU-limited at lower resolutions.
At 1440p, workloads are usually more balanced, allowing both CPU and GPU to work efficiently.
At 4K, the GPU handles most of the workload, which makes GPU bottlenecks far more common.
A comparison table should be placed here showing resolution versus CPU load, GPU load, and typical bottleneck behavior.
| Resolution | CPU Load | GPU Load | Typical Bottleneck |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1080p | High | Medium | CPU bottleneck |
| 1440p | Medium | Medium | Balanced |
| 4K | Low | High | GPU bottleneck |
When a Bottleneck Calculator Is Most Useful
A bottleneck calculator is useful before upgrading parts, when building a new PC, when performance feels lower than expected, and when mixing old components with new ones. Using the tool early helps avoid wasted money and poor upgrade decisions by highlighting possible mismatches in advance.
Most common use cases:
- Before upgrading CPU or GPU
- When building a new PC
- When FPS is lower than expected
- When combining old and new hardware
How to Fix or Reduce Bottlenecks
Not all bottlenecks require hardware upgrades. In many cases, performance can be improved by adjusting graphics settings, increasing resolution, closing background programs, updating drivers, enabling proper RAM profiles, and improving system cooling.
If performance remains limited after optimization, upgrading the component causing the bottleneck is the smarter solution.
Optimization steps to try first:
- Increase resolution or graphics settings
- Close unnecessary background apps
- Update drivers
- Enable correct RAM profiles
- Improve system cooling
Smart Upgrade Decisions
Upgrading without understanding system balance often leads to disappointment. If results indicate a CPU bottleneck, upgrading the processor or platform is usually more effective. If the system is GPU-limited, upgrading the graphics card makes more sense.
If memory is the issue, increasing RAM capacity or speed can help. Balanced upgrades almost always deliver better results than isolated upgrades.
Bottleneck Calculator vs Manual Testing
A bottleneck calculator provides fast estimates and planning insight. Real-world testing through benchmarks and monitoring tools shows exact system behavior.
Both methods are useful.
Use a calculator for planning and comparisons.
Use benchmarks for exact performance testing.
Together, they provide better insight.
Balanced PC Build Guidance
Balanced systems deliver smoother gameplay, more stable FPS, and better overall responsiveness. Matching component levels, avoiding extreme mismatches, and choosing the right resolution all help reduce bottlenecks.
A balanced PC almost always feels better to use than an unbalanced, powerful one
Conclusion
A bottleneck calculator is a practical tool for understanding PC performance balance. It helps users make smarter decisions when upgrading or building a system. By identifying which component is limiting performance, you can avoid unnecessary spending. This leads to better value and smoother performance.
However, bottleneck results should always be treated as estimates, not guarantees. Real-world performance depends on games, settings, drivers, and system usage. For best results, combine calculator insights with benchmarks and real testing. Use this tool as guidance to optimize and upgrade with confidence.
